Pleural mesothelioma, a rare cancer affecting the pleura (the protective lining of the lungs), is often linked to asbestos exposure. Unlike lung cancer, which originates in the lung tissue itself, pleural mesothelioma develops in the pleural membranes. This blog provides a science-backed overview of malignant pleural mesothelioma, its diagnosis, stages, and treatment options, tailored for readers in the USA.
What Is Pleural Mesothelioma?
Pleural mesothelioma, or mesothelioma of the pleura, arises when malignant cells form in the pleural layers. The pleura consists of two membranes: the visceral layer (covering the lungs) and the parietal layer (lining the chest wall). This cancer is categorized as diffuse pleural mesothelioma due to its tendency to spread widely across the pleura. Approximately 2,500–3,000 new cases are diagnosed annually in the USA, primarily in individuals with prior asbestos exposure.
Key Fact: Pleural mesothelioma accounts for 80–90% of all mesothelioma cases, making it the most common form.
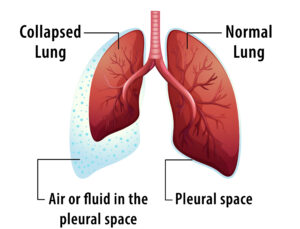
Is Pleural Mesothelioma Lung Cancer?
No. While both cancers affect the thoracic cavity, pleural mesothelioma is not lung cancer. Lung cancer develops in lung tissue, whereas mesothelioma originates in the pleura. Their treatment protocols and prognoses differ significantly.
Also Read: Neo Guide to Mesothelioma: Modern Insights into Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of pleural mesothelioma is asbestos exposure. When inhaled, asbestos fibers lodge in the pleura, causing inflammation, DNA damage, and cellular mutations over decades. Occupations with high exposure risks include construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing.
Scientific Evidence:
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies asbestos as a Group 1 carcinogen.
- Secondary exposure (e.g., through family members’ contaminated clothing) can also pose risks.
Other risk factors include radiation therapy to the chest and genetic predisposition, though these are less common.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Symptoms often emerge 20–50 years post-exposure, delaying diagnosis. Early signs mimic common respiratory issues:
- Persistent dry cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Unexplained weight loss
Advanced stages may involve pleural effusion (fluid buildup) and systemic symptoms like fatigue.
Pleural Mesothelioma Diagnosis
Diagnosis requires a multi-step approach:
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays or CT scans detect pleural thickening or effusion.
- PET scans identify metastatic spread.
- Biopsies:
- Thoracoscopy-guided tissue sampling confirms malignancy.
- Histopathology:
- Subtypes (epithelioid, sarcomatoid, biphasic) are identified, influencing prognosis.
Note: Early referral to a specialist improves diagnostic accuracy.
Also Read: Teaching Children About Mesothelioma
Pleural Mesothelioma Stages
Staging determines disease extent and guides treatment. The TNM system (Tumor, Nodes, Metastasis) is used:
- Stage 1: Localized to one side of the pleura.
- Stage 2: Spread to nearby lung tissue or lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Involves the chest wall, diaphragm, or distant lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: Metastasized to distant organs.
Treatment Options Based on Stages
Early-Stage (I–III):
- Surgery: Extrapleural pneumonectomy (removing the affected lung and pleura) or pleurectomy/decortication (removing the pleura).
- Multimodal Therapy: Combining surgery, chemotherapy (e.g., cisplatin/pemetrexed), and radiation.
Advanced-Stage (IV):
- Palliative Care: Focuses on symptom relief via thoracentesis (fluid drainage) or pain management.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs like nivolumab and ipilimumab show promise in clinical trials.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Prognosis remains challenging due to late diagnosis. Median survival ranges from 12–21 months, depending on stage and cell type. Epithelioid subtypes generally respond better to treatment.
Prevention and Legal Recourse
Prevention centers on asbestos avoidance:
- Follow OSHA workplace safety guidelines.
- Test older homes for asbestos before renovation.
In the USA, patients may pursue legal compensation through asbestos trust funds or lawsuits.
Also Read: Is Mesothelioma Contagious? Separating Fact from Fiction
Conclusion
Pleural mesothelioma is a complex cancer with distinct characteristics separating it from lung cancer. While treatment advances like immunotherapy offer hope, early detection and asbestos exposure prevention remain critical. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
This blog is for informational purposes only. For medical advice, consult a doctor or trusted source like the American Cancer Society.
1 thought on “Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment”